Scenario 3: Building Master Data
Version 8.0.0.490
Tutorial
Scenario: Building Master Data Step
1: Configuring Master Data Matching and Merge Rules Specifying
Matching and Merge Rules Step
2: Map Master Data Columns for Querying Step
3: Execute Sample Queries A major benefit of SDF is the
ability to create and maintain master data from data across multiple data
sources in a distributed manner. SDF does this without making copies of data in
a central location while easily and seamlessly integrating master data with
operational data without putting a query load on the underlying data sources.
This is accomplished by taking advantage of built-in data federation and record
linking features in SDF. The master data generation process
is based on finding matching attribute values for master data entity
attributes. Master data entities can be simple or complex. Simple entities may
have one or two attributes, whereas a complex entity may have other entities as
attributes. An example of a simple entity in a patient management system can be
a contact email address or phone number. An example of a complex entity is a
patient having a name, address, email, and phone number as attributes. Internally, the master data build
process follows these steps for each entity type configured for master data
generation: 1. Binning
entities based on a selected subset of entity attributes using exact matches of
raw or fuzzy versions of the attribute values. 2. Linking
records within each bin. 3. A
detailed scoring of entities in a bin based on closeness of attribute values
using edit distance algorithms. 4. Grouping
and filtering matches based on a given cutoff threshold (records in the same
group are considered as belonging to the same entity). 5. Merging
matching entities based on given merge rules to generate a master record for
that entity. This documentation
serves as an example scenario for master data management and integration using
sample data sources included in the SDF media. . 1. Configure
master data matching and merge rules to build master data. 2. Map
master data columns for querying. 3. Execute
sample queries on master data. The initial step in configuring MDM is defining the MDM
entity and its essential entity attributes in terms of business mapped
dictionary column names. These entity attribute columns will be available later
as binning attributes for use during the MDM matching configuration. In order to properly link records for master data
generation, you need to make sure the entity column information is accurate for
the entity and has all of the columns you need. This helps creating links using
all the necessary attribute data. ·
Go to the ‘Dictionary Mapping’ tab and click
‘Edit Entity Data’ at the bottom of the window. To define an entity, you need to make sure that the
attributes that define a unique field are all in the center pane under the
proper entity. For example, if the combination of the LastName, FirstName and
DOB fields define a unique PERSON entity, those three fields become attributes
for the PERSON entity and should be added to the center pane. The following table contains the entity you will need for
this scenario and the attributes that populate that entity. Entity
Name Attributes PERSON FirstName, LastName, DOB To create an entity, click ‘New Entity’. Enter a name for
the entity and, if necessary, a description. Entities will auto-populate with
one attribute when created. The PERSON entity included with the installation has the
wrong elements defining the entity based on your mapping. You need to replace
FIRST_NAME and FAMILY_NAME with the FirstName and LastName elements we mapped. ·
Using the ‘Dictionary Elements box, search for
the attributes that define the entity and add them to the ‘Attributes’ box by
selecting them and clicking the left arrow. Remove any incorrect or unnecessary
attributes by selecting them and clicking the right arrow. Your resulting entity should look like the PERSON entity in
the first screenshot shown above. You can close this window after you have
ensured the necessary entities are there. With the EIQ Indexed Adapters configured, the EIQ Federation
Server created, and the entities defined, you can now create a Link Index for
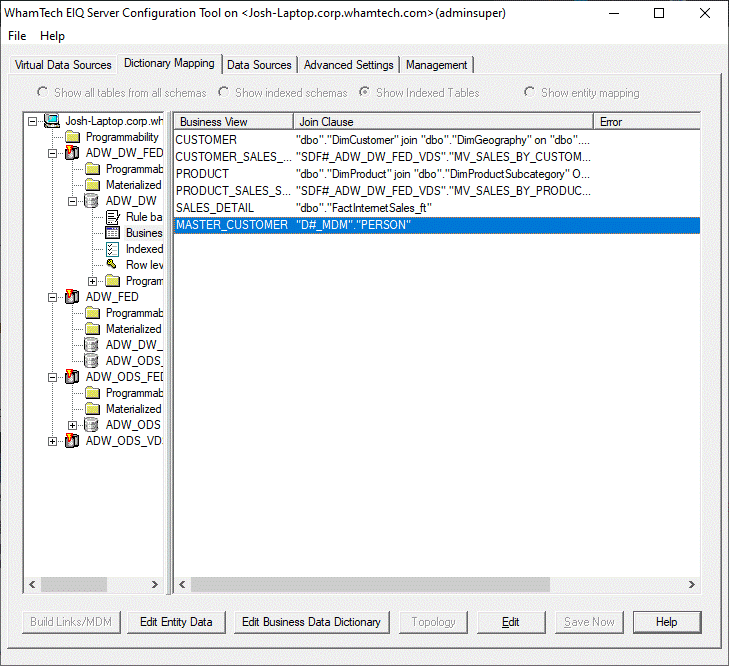
the master data. Within the ‘Dictionary Mapping’ tab: ·
Expand the server node in the left pane and find
ADW_FED. ·
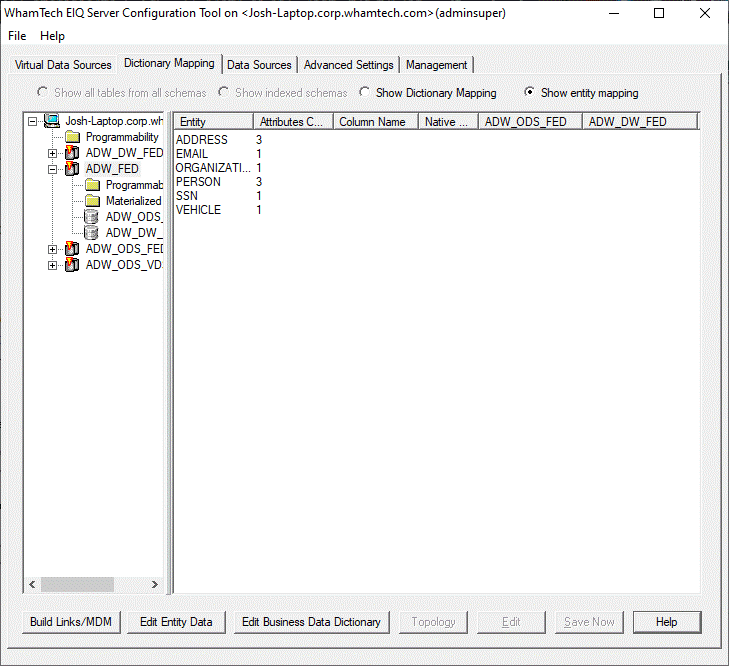
Select ‘Show entity mapping’ (below the advanced
settings and management tabs). This menu shows the entities defined, the number of
attributes defining those entities, and the remote servers under the EIQ
Federation Server. ·
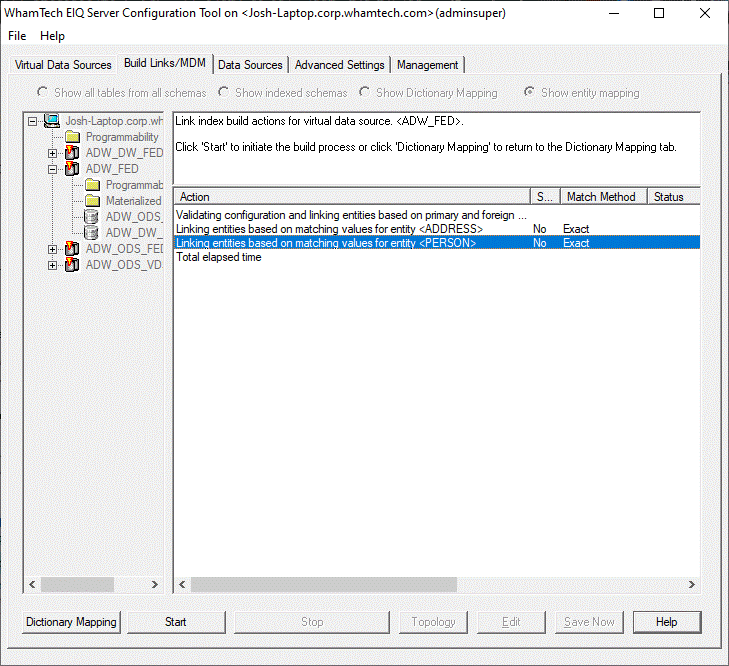
Click ‘Build Links/MDM’ in the bottom left. This shows the available entities on the EIQ Federation
Server. The only entities that appear here are entities that have mapped
attributes on the adapters. For instance, the screenshot above shows more than
three entities, however those entities have no mapped attributes on the
adapters, so they are not selected for linking and master data building. All
matching rules are set to ‘Exact’ by default. You will need to apply fuzzy matching to the PERSON entity.
Fuzzy matching is a technique that assists in record linkage. It works with
matches that may be less than 100% perfect when finding correspondences between
segments of a text and entries in a database of previous translations. Rather
than having multiple files for one person, use it to find similarities between
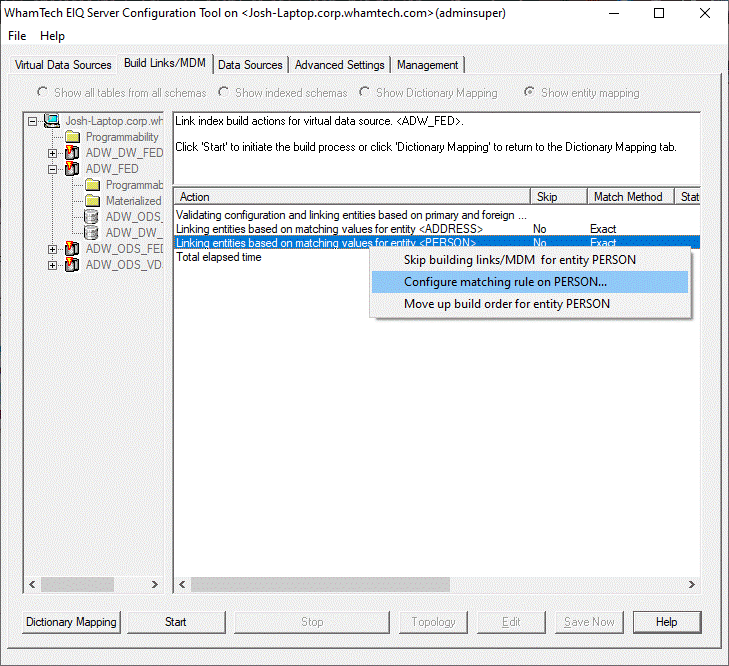
data sources and match together records into one master person index. ·
Select the entity where you need to apply Fuzzy
Matching, for example, the PERSON entity. ·
Right Click on the Entity Name ·
Select “Configure matching rule on ‘PERSON’”. The next window will ask which type of fuzzy matching you
want to use - Probabilistic or Non-Probabilistic. ·
Select "Non-Probabilistic". ·
Then, select CUSTOMER from the dropdown menu.
This tells the process to use the attributes from the CUSTOMER business object
we created. Note: Probabilistic Match is currently in a beta
stage. This feature will be available shortly and is a more advanced way of
matching. Ignore it for now. The next window is for configuring the matching rule. ·
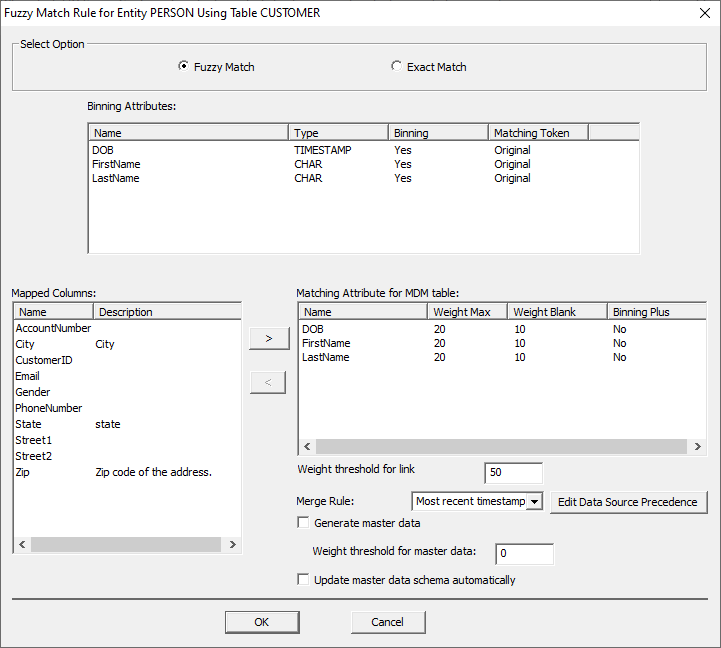
Select “Fuzzy Match” in the ‘Select Option’ box. The tool automatically populates entity attributes as Binning
Attributes. You can select the Binning Attributes and modify them as per
requirements. For this scenario, we will keep it simple and leave them as
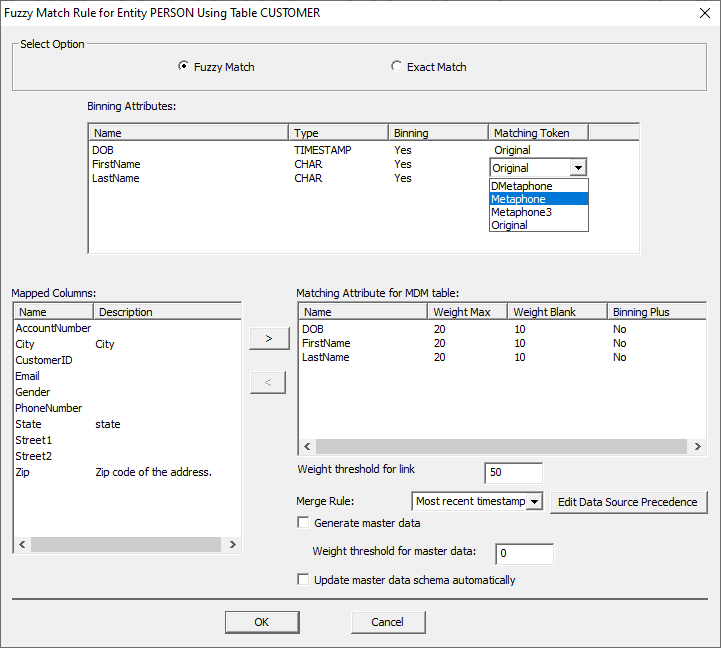
default with the exception of the Matching Tokens. Now: ·
Change the Matching Token for FirstName and LastName
from 'Original' to 'Metaphone'. ·
Do this by double-clicking 'Original' and
selecting 'Metaphone' from the drop-down menu. Note: Metaphone3 requires manually installing and
enabling the Metaphone3 extension. This will be enabled automatically in future
releases. ·
Add the Matching Attributes for the MDM Table.
This should be all the columns in your master data set you want to merge. Add
the following by selecting them in the ‘Mapped Columns’ box and clicking the
right arrow. To remove an attribute, select it in the ‘Matching Attribute for
MDM table’ box and click the opposite arrow. ·
Add Weight Max for each attribute and Weight
Blank as per the requirement. Max Weight is the maximum value possible for that
attribute, exact match gets the full weight and fuzzy logic gets a fraction
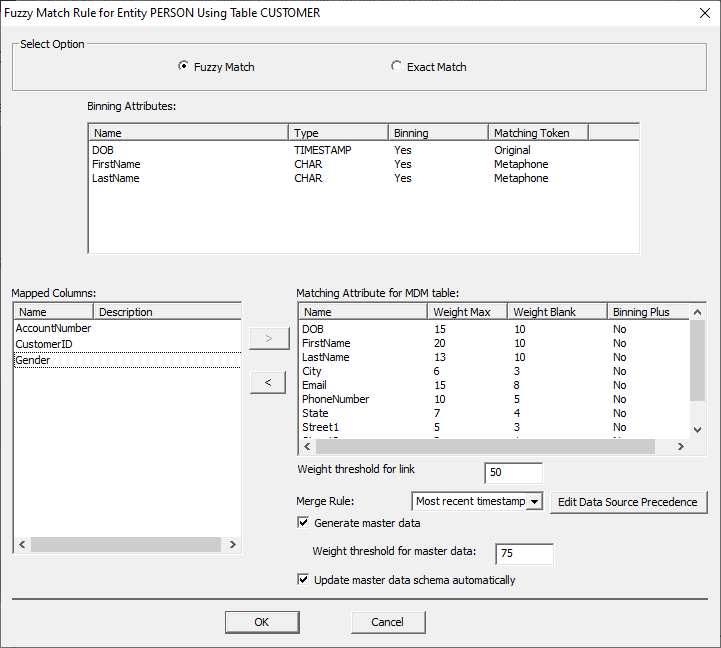
based on the calculated distance. Name Weight
Max Weight
Blank Binning
Plus DOB 15 10 No FirstName 20 10 No LastName 13 10 No City 6 3 No Email 15 8 No PhoneNumber 10 5 No State 7 4 No Street1 5 3 No Street2 2 1 No Zip 3 2 No ·
Leave Weight Threshold for link as the default
of '50'. (This is the threshold required for a link to be created between the
records). ·
Select “Generate master Data”. o
Leave the Weight Threshold for master data as
'75'. (This is the minimum total weight required for a record to be merged). o
This uses the raw value not a percentage. o
Merge rule: Most recent timestamp -- Tells it to
get the most recent record when merging records for MDM. o
Select “Update master data schema
automatically”. §
It automatically updates the schema if new
attributes are added after initial creation. ·
Click “OK” to close the window. Once matching rule configuration is complete, you can start
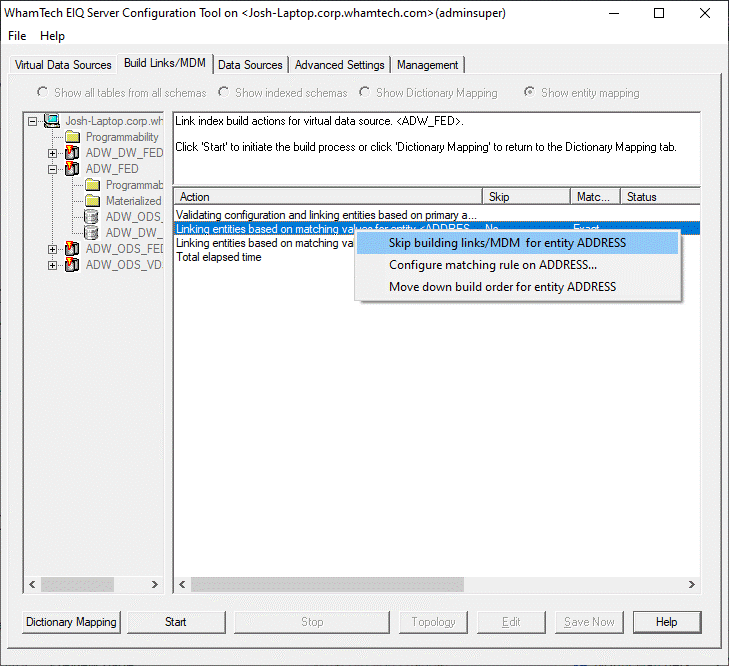
the build process. Before that, however, any additional entities you may want
to select to skip because they are unnecessary. ·
Right-click an entity and select 'Skip building
links/MDM for entity....' ·
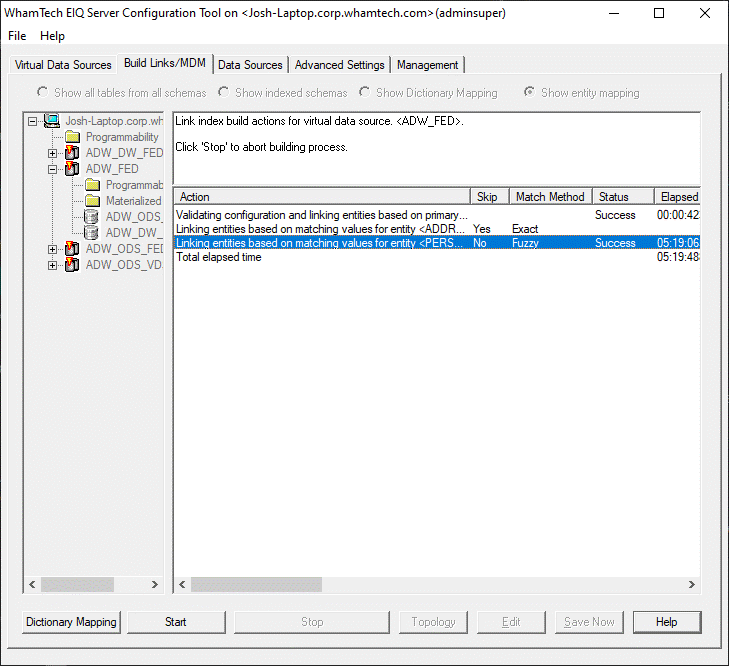
Click 'Start' to generate master data. ·
A successful build will look like the screenshot
below. Now that the index has been built successfully, the generated
master data needs to be mapped to a business data view. ·
Click ‘Dictionary Mapping’ in the bottom-left to
return to the mapping screen. ·
Go to the ADW_ODS_FED_VDS or ADW_DW_FED_VDS,
expand the tree, and click on the grey node. ·
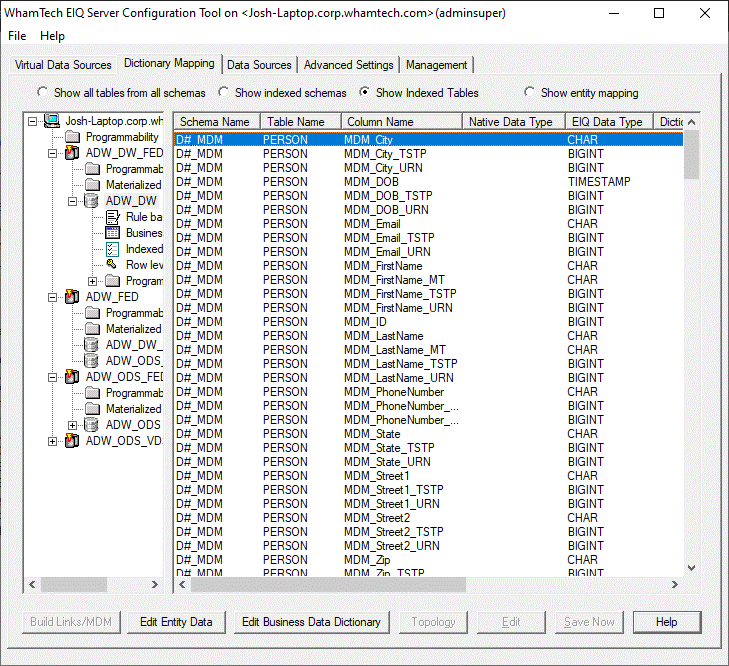
Make sure ‘show indexed tables’ is selected. The “D#_MDM” schema has been added and a PERSON table has
been created with the selected matching attributes. The master data generation
process created an entirely new schema for the master data. The same schema is
available in the ADW_ODS_FED_VDS and ADW_DW_FED_VDS. In real use scenarios,
every VDS that was connected to the EIQ Federation Server with the same
entities when master data is generated will have the new Master Data schema. Now users can add Dictionary Attributes to their master data
columns to create a business data view. Follow the procedure below to add
Dictionary Names to the ADW_DW_FED_VDS Master Data: ·
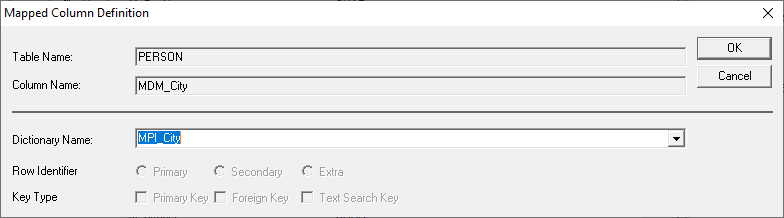
Select Column MDM_City -> right-click and
select 'Edit'. ·
The Mapped Column Definition window opens. ·
Now enter the Dictionary Name: “MPI_City”. MPI
is used to specify that it is the Master Person Index. Depending on a
particular industry, users may want to define this differently. MCI could
indicate a Master Customer Index, or MPI could be defined as a Master Patient
Index. For the tutorial, we are just calling it a Master Person Index. Master
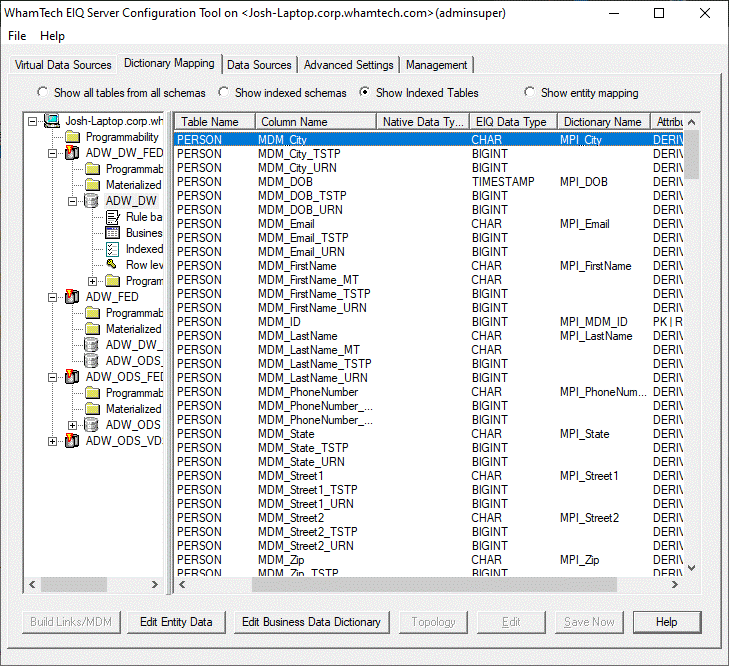
Data Column Name Dictionary
Name MDM_City MPI_City MDM_DOB MPI_DOB MDM_Email MPI_Email MDM_FirstName MPI_FirstName MDM_LastName MPI_LastName MDM_ID MPI_MDM_ID MDM_PhoneNumber MPI_PhoneNumber MDM_State MPI_ State MDM_Street1 MPI_ Street1 MDM_Street2 MPI_ Street2 MDM_Zip MPI_Zip dim.Customer MDM_ID_PERSON MDM_ID_Customer You may notice from the mapping process that a new column
was also inserted into the dim.Customer table. This MDM_ID column is a derived
column inserted by the process in order to keep track of records that have been
matched and merged during the MDM build process. ·
Click “Save Now” to save the business data view
mapping. The final step is creating a new business view for the MDM.
On each adapter: ·
Go to the Business View creation tab. ·
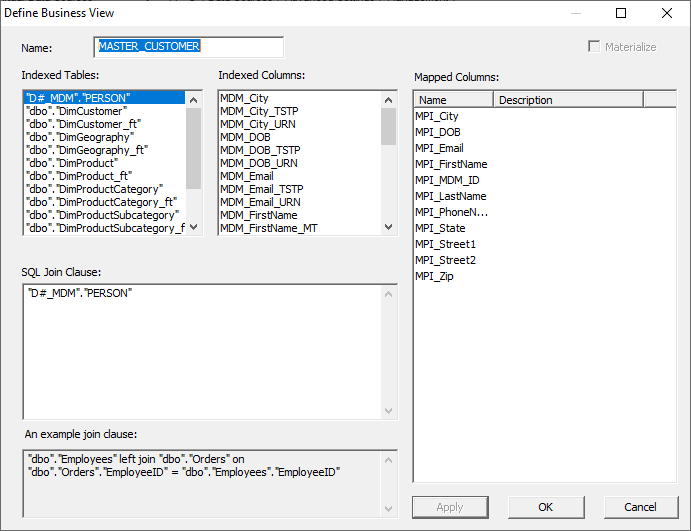
Create a new Business View as follows: o
Name the Business Object. o
Select "D#_MDM"."PERSON"
from the list of tables. o
Add it to the Business View clause. o
Verify the correct mapped columns are available. o
Click "Apply" and then "OK"
to close the window. The new Business View will appear in the list on the main
tab. Make sure to perform the same setup on the ADW_ODS_FED_VDS.
You'll need to map the MDM columns to the business data view, and then create
the business view using the exact same table in the above process. Note: The MDM_ID_PERSON column inserted by MDM in ADW_ODS_FED_VDS
is in the vCustomerDemographics table. That will need to be mapped to
MDM_ID_Customer. This completes the MDM setup and creation process. Using the
PGAdmin tool, connect to the EIQ Federation Server and make queries as usual. To query on the master data, connect to the EIQ Federation
Server where the master data was created. Open PGAdmin and connect to the
ADW_FED. You should notice the new MASTER_CUSTOMER table is available. That's
where our MDM will be. Note: The following screenshots show the query
connection as ‘AdminSuper Connection’. For clarification, this should be the
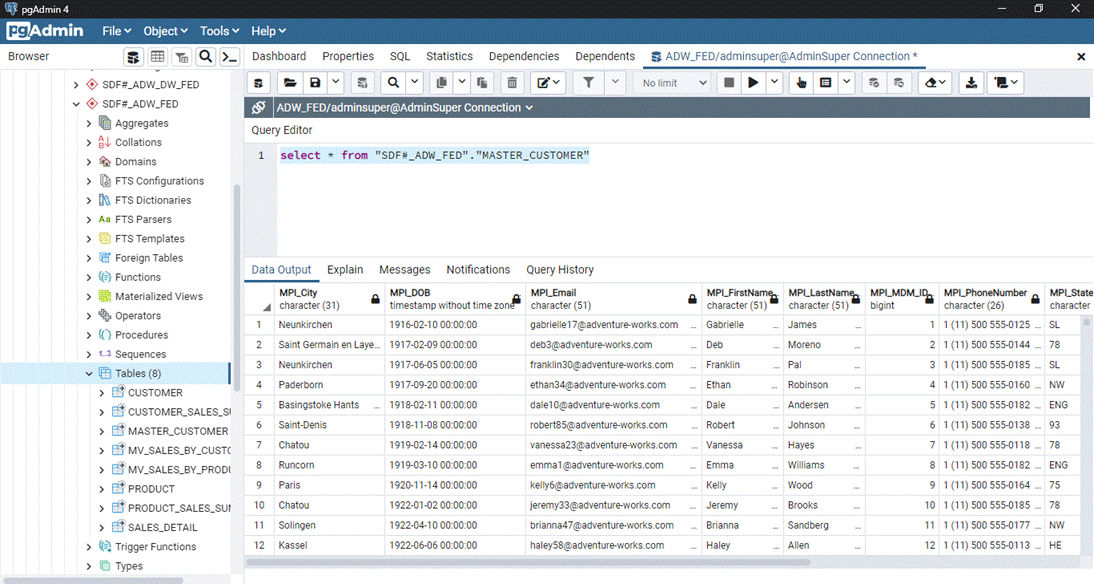
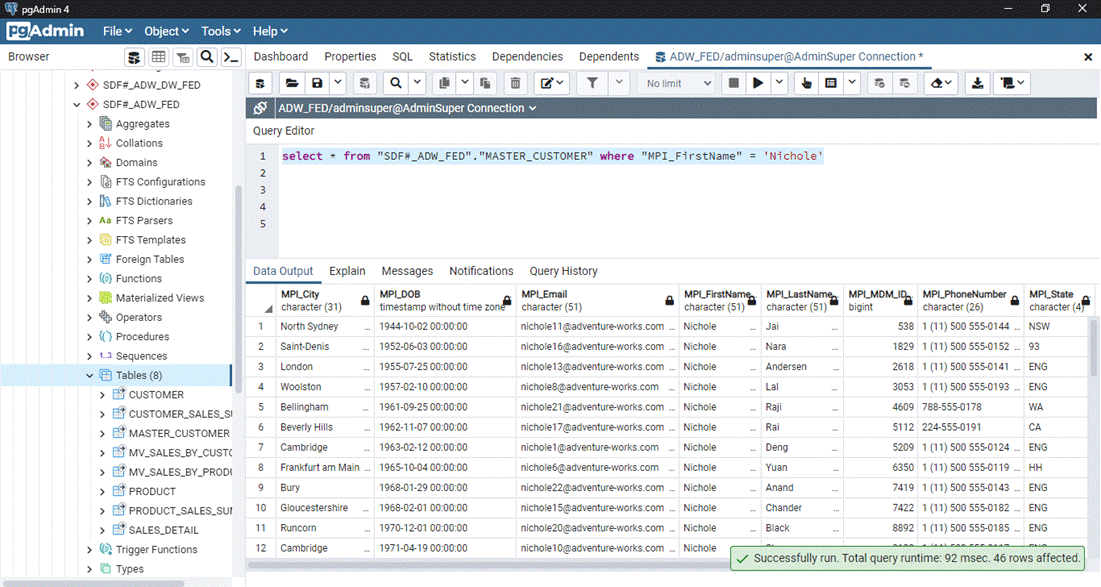
‘ConfigAdmin Connection’ created in Scenario 1. Try the sample query SELECT * FROM
"SDF#_ADW_FED"."MASTER_CUSTOMER" . This query shows all of the master data columns mapped to
the business data view. Now try the query SELECT * FROM
"SDF#_ADW_FED"."MASTER_CUSTOMER" WHERE
"MPI_FirstName" = 'Nichole' The MDM shows a limited number of
results. Due to the MPI_MDM_ID column, in instances like Nichole Nara we can
see that two records have been marked as the same record. We can query the
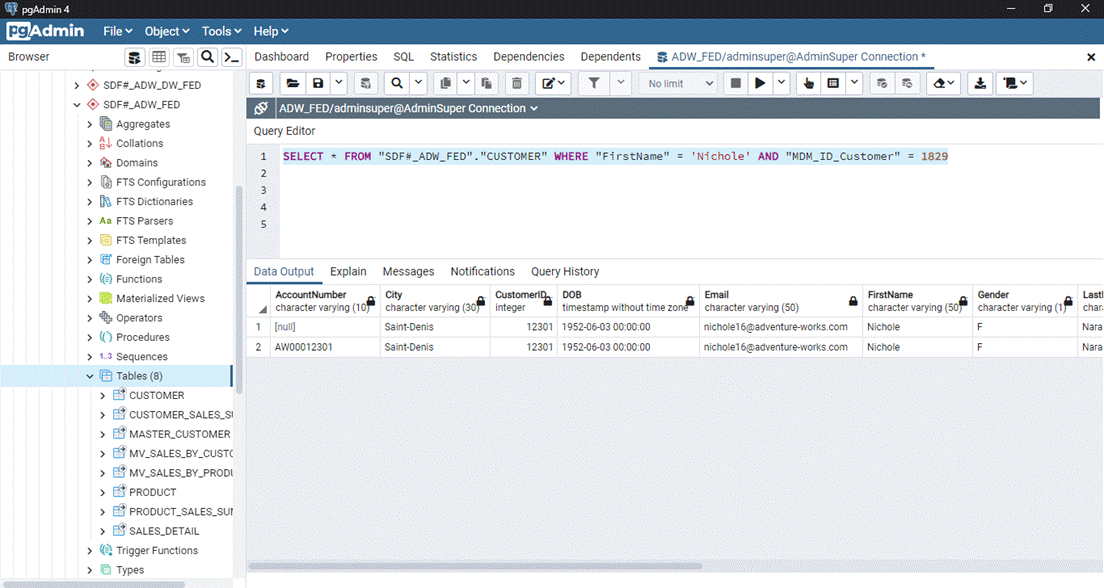
original Federation Server data from the same window to see how much changed. Execute SELECT * FROM
"SDF#_ADW_FED"."CUSTOMER" WHERE "FirstName" =
'Nichole' AND "MDM_ID_Customer" = 1829 In this screen we see that there were multiple records for
Nichole Nara. The master data was able to link these records together and merge
them as the same person. You can see in the MDM_ID_Customer column which
records the master data generation process flagged as the same record. That concludes Scenario 3. Feel free to continue running
queries on the Master Data, and even try combining Master Data queries with the
transactional base table queries to get the full power of federated EIQ Hybrid
Adapters with MDM built on them. Tutorial
Scenario: Building Master Data
Step
1: Configuring Master Data
Matching and Merge Rules
Editing Entity Data


Specifying Matching and Merge Rules


Step 2: Map Master Data Columns for Querying
Step 3: Execute Sample
Queries
Copyright
© 2023 , WhamTech, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is
provided for information purposes only and the contents hereof are subject to
change without notice. Names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
